Introduction
Regenerative agriculture is rapidly gaining attention as a transformative approach to farming. Unlike conventional methods, it focuses on improving soil health, increasing biodiversity, and reducing carbon footprints. This article explores the principles, benefits, and global adoption of regenerative agriculture.
Principles of Regenerative Agriculture
- Soil Health and Carbon Sequestration:
- Key Practice: No-till farming and composting.
- Impact: Enhances microbial activity and locks carbon in the soil.
- Crop Diversity:
- Key Practice: Rotational planting of diverse crops.
- Impact: Improves nutrient cycling and pest control.
- Water Management:
- Key Practice: Drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting.
- Impact: Optimizes water usage and prevents soil erosion.
Benefits
Environmental: Reduction in greenhouse gases.
Economic: Increased yield and cost savings for farmers.
Social: Healthier food production for communities.
Adoption Worldwide
Country Example: Australia
- Farmers are adopting regenerative grazing to restore grasslands.
Case Study Example:
A farm in the U.S. restored 500 acres of degraded soil through composting and crop rotation, increasing yield by 20%.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1:
A pie chart showing the global adoption of regenerative farming.
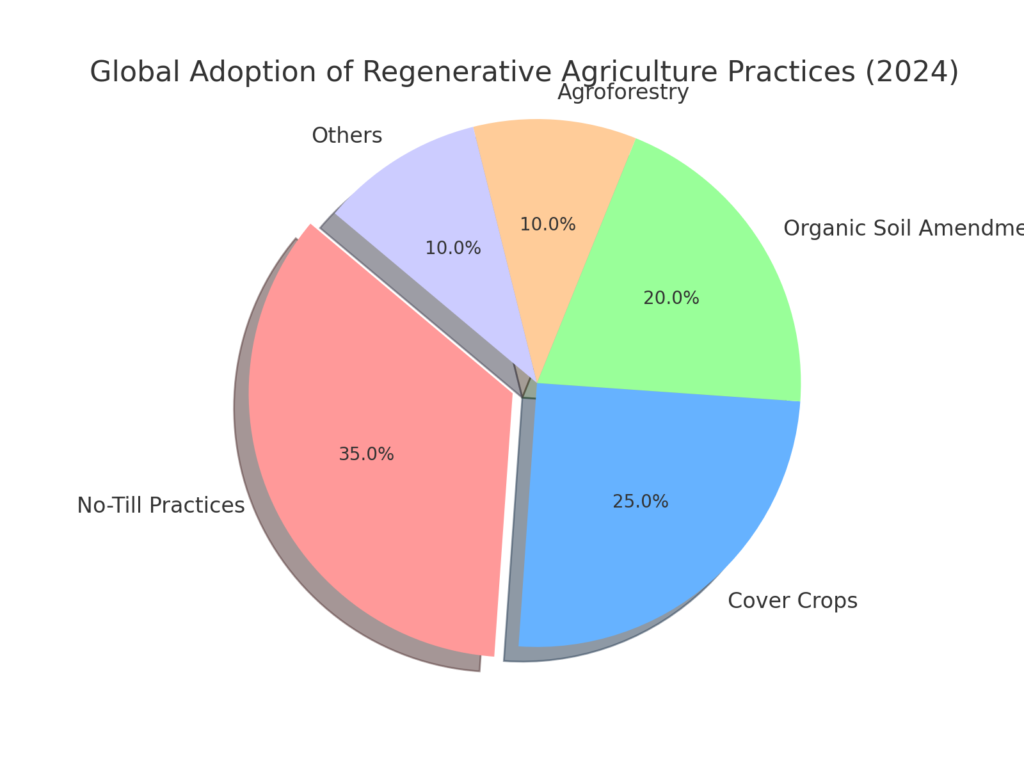
Table 1: Comparison of Conventional vs. Regenerative Agriculture
| Metric | Conventional Farming | Regenerative Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | High | Low |
| Soil Fertility | Decreasing | Increasing |
| Biodiversity | Minimal | High |
Conclusion
Regenerative agriculture is not just a method but a movement towards sustainability. By adopting these practices, we ensure food security and environmental health for future generations.


